Services on Demand
Article
Indicators
Related links
-
 Cited by Google
Cited by Google -
 Similars in Google
Similars in Google
Share
South African Journal of Higher Education
On-line version ISSN 1753-5913
S. Afr. J. High. Educ. vol.38 n.1 Stellenbosch Mar. 2024
http://dx.doi.org/10.20853/38-1-6284
SPECIAL SECTION
A systematic review of key success factors in postgraduate studies
L. I. NwosuI; T. SegotsoII; N. B. EnebeIII; M. NyakuwanikaIV
ISchool of Accounting Science, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
IISchool of Accounting Science, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
IIISchool of Commerce Education, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
IVDepartment of Accounting, Great University of Zimbabwe, Harare, Zimbabwe
ABSTRACT
BACKGROUND: Massification of higher education and growth in undergraduate students has propelled a wave of students seeking advanced degrees. Increasing numbers of postgraduate students reflect the performance of Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) and highlight the need to study key elements affecting postgraduate academic success
PURPOSE: This systematic literature review (SLR) aims to identify key success factors related to postgraduate studies
RESEARCH APPROACH: The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines were used to guide the reporting of this review. Articles in ScienceDirect, Jestp.com, Ed.gv, Tandfonline.com, Oup.com, Springer.com, Researchgate.net, Sagepub.com, Wiley.com, Alt.ac.uk, and Stor.org were searched between January 2013 and January 2023
RESULTS: A final 28 studies from 14 countries were reviewed to provide a holistic assessment of major factors affecting postgraduate academic success. The most common success factors in postgraduate studies are teaching and learning methods, quality research supervision, research capacity building, library services, Postgraduate Student Office workshops, and student characteristics. Limitations within some factors were also reported
CONCLUSION AND IMPLICATION: The study concluded that postgraduate students' ability to function effectively depends on adequately implementing and managing critical and complex factors. The results of the study will inform postgraduate programme practitioners
Keywords: key success factors, postgraduate studies, postgraduate students, higher education institutions, universities
INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND
The higher education system worldwide has changed due to the development of knowledge-based societies; as a result, many universities are actively advertising their postgraduate programmes (Baporikar 2022). A tsunami of students seeking credentials has been sparked by the massification of higher education and an exponential expansion in student enrolment (Muthukrishnan et al. 2022). The rise in postgraduate enrolments at most universities worldwide confirms the performance of HEIs (Singh 2018), but has also drawn attention to the importance of comprehending the key elements that support academic achievement in postgraduate study. However, high attrition and low graduation rates among students have threatened the critical success and performance of the higher education system (Muthukrishnan et al. 2022).
Higher educational systems are challenged by the changes in higher learning (Areiqat et al. 2021). Universities are under pressure to raise the standard of higher education offered to graduates since they are seen by the community as essential providers of information (Salimi, Bekkers, and Frenken 2016). One of the main issues for HEIs and governments at the national and international levels is producing graduates of high calibre, particularly in light of the worldwide coronavirus pandemic emergence (Areiqat et al. 2021). According to Muthukrishnan et al. (2022), postgraduate students are urged to immerse themselves in a research environment to ensure prompt completion of their research journey and timely graduation. However, due to the challenges they face in their lifetime journey, many postgraduate students are unable to finish their studies and have a high dropout rate (Hadi and Muhammad 2019). According to Singh (2018), many universities worldwide cannot assist their students with dropout issues because they find it challenging to identify the essential success criteria and unique traits of postgraduate students. This is because concerns about integrating all crucial success factors in postgraduate studies at various universities on the African continent are essential for improving the atmosphere for good teaching, learning, and research.
Several important aspects typically influence the academic success or failure of postgraduate students. Self-reliance, financial possibilities, and academic freedom are all elements that help postgraduate students succeed academically (Baporikar 2022). According to a Malaysian study by Young et al. (2013), postgraduate international students' prior academic achievement, psychological well-being, satisfaction with life in the new level of academic environment, and intellectual competence all play a role in their academic success. However, Ham-Baloyi and Jordan (2016) state that the research supervisor may be unable to mentor the postgraduate research student if there is a communication gap between them. In their simplest terms, these key elements have been identified as critical in student academic success through literature reviews. However, it is still unclear whether there are critical components that guarantee that postgraduate students are progressing toward achieving their academic objectives.
The knowledge-based society and the academic achievement of postgraduate students have greatly benefited from the research capacity and development initiatives at universities, particularly in postgraduate programmes (Muthukrishnan et al. 2022). As a result, many universities are actively promoting their postgraduate programmes. According to Muthukrishnan et al. (2022), postgraduate students' academic success is greatly influenced by their capacity for self-management, institutional support, and student research abilities. In a 2017 study, Soumana and Uddin (2017) discovered that PhD students perceived their advisers as obstacles to completing their theses. Lynch, Salikhova, and Salikhova (2018) concurred with these conclusions, confirming that graduate students' supervisors gave them little assistance, autonomy and competence. On the contrary, the results of Muthukrishnan et al. (2022) revealed that supervisory techniques did not improve students' motivation or research skills.
On the other hand, the student's institution plays a significant role in graduate research studies, particularly regarding access to library resources (Rasul and Singh 2017). While that is the case, Sidhu et al. (2013) noted that postgraduate students in Malaysia indicated their discontent with institutional support and demanded fully operational research centres. According to Rasul and Singh (2017), 90.1 per cent of college students believe having access to a well-stocked library is crucial for facilitating research.
Although a large body of literature has explored the connections between critical factors and academic success, limited research has been conducted on the Systematic Literature Review SLR approach, particularly concerning postgraduate students. This study fills the research gap in the literature by conducting an SLR on the critical success factors associated with postgraduate studies. Thus, this article sets the following research question through SLR: What are the key success factors that contribute to academic success in postgraduate studies? This research aims to advance the field of postgraduate student development. The study draws on existing literature findings, but sheds more insight on how key elements for academic success in postgraduate courses can be applied to the global international higher education market. The findings will be useful information for practitioners currently teaching in postgraduate programmes. The remaining sections of this article are divided into the literature review, research strategy, findings and discussion, conclusions, consequences, limitations, and potential future research directions.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Postgraduate research plays a crucial role in higher education, with academic performance being influenced by various factors. Moreover, various key themes that were identified emerged from the literature. These themes include university reputation, programme reputation, programme qualification, administrative aspects, country or city characteristics, environment, information availability, and career plans (Van Rooij, Fokkens-Bruinsma, and Jansen 2021). Institutional factors, such as adequate access to equipment, suitable working spaces, financial support, library facilities, and technical support, can also impact students' academic performance (Molson 2022). Furthermore, the importance of personal factors such as motivation for graduate work, interest in performing research, dealing with ambiguity, a sense of balance in life, realistic expectations of graduate work, and the ability to handle the demands of graduate work (Han, Gulanowski, and Sears 2022). According to Honig and Rainey (2019), supervisors also play a significant role in fostering academic success, as they provide mentoring skills, guidance, and student support. Experience, such as having a supervisor with the necessary subject knowledge and skills, is essential in postgraduate research (Alalwan et al. 2019). Moreover, it was found that non-academic criteria, such as student welfare and well-being, mentorship, employable skills training, and inclusive research communities, also significantly impact postgraduate student choices and success (Frantz et al. 2022; Kismihók et al. 2022). Financial considerations were consistently identified as the most influential factor in determining whether a student would pursue postgraduate studies (Sheldon et al. 2021).
In light of the above, students are confronted with the common issues of conducting useful scientific research. It indicates the need for improved research skills training. When students have undergone tutoring, it will help them conduct research independently under minimal supervision. Meanwhile, students' attitudes towards research can also impact their performance, as they may hesitate to take time away from studies or seek feedback from seniors and colleagues. In terms of performance, students' self-efficacy can be a key factor, as they are confident in their ability to solve complex problems and deal efficiently with unexpected events.
Moreover, universities should provide comprehensive information about their programmes and create a supportive environment for their postgraduate students. It is also important to foster inclusive research communities and provide mentorship and employable skills training to enhance postgraduate student success. Furthermore, the research ambience in a faculty can stimulate their work and provide symposium and seminar programmes. It is worth noting that even though the literature reviewed has identified factors that can improve academic performance and contribute to the overall quality of higher education in research, it is still unclear which factors are essential. Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) should pay attention to the identified factors in order to improve the overall quality and effectiveness of postgraduate education.
RESEARCH APPROACH
Literature search
The ScienceDirect, Jestp.com, Ed.gv, Tandfonline.com, Oup.com, Springer.com, Researchgate.net, Sagepub.com, Wiley.com, Alt.ac.uk, and Stor.org databases were searched between January 2013 and January 2023. The search keywords used included: critical success factors for postgraduate students, success factors in postgraduate studies, postgraduate students, success factors for postgraduate studies in Higher Education Institutions, success factors for postgraduate studies in universities, important factors for success in higher education, and difficulties in completing postgraduate studies.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The following inclusion and exclusion guidelines were used, as shown in Table 1.
Study selection and data extraction
The initial search retrieved 435 publications, which was reduced to 343 after 92 duplicate publications were removed. All potentially relevant publications were accessed in full-text format. The publications underwent screening to include articles, book chapters, and conference papers before 89 full-text publications were eligible for further assessment. A title and abstract screening were conducted on the 89 full-text publications using the eligible criteria in Table 1. A final 28 papers were included for review, as shown in Figure 1 and Table 2. The data extraction was performed by two authors who double-coded 40 per cent of the 28 full-text publications to establish consistency before adjusting the strategy and individual code and checking the remaining papers. Conflicting decisions were discussed and resolved. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) was used to guide the reporting of this review (see Figure 1). PRISMA is a data collection technique that helps bridge research gaps to correlate existing literature through an SLR approach.
In Table 2, the purpose was to show the various sources reviewed, the number of studies per source, and the number of studies included or excluded from this study.
Table 2 explicitly shows the number of publications included and excluded in this study; Figure 2 is a PRISMA flowchart. The link between these two was that they both give a clear understanding of how the study's reviewed materials were selected and used. Figure 2 shows a diagrammatic representation of the processes involved in the inclusion and exclusion criteria used in this study. It was provided to clarify the steps taken to arrive at the final reviewed papers.
Data synthesis
The results were analysed qualitatively, and a synthesis method was applied. The individual significant successes discovered were coded and categorised using a content analysis method. One of the authors conceptualised and categorised the data, and another author later evaluated its theoretical applicability. Any discrepancies in the categories' definition, formulation, and integration were settled through debate and additional examination of the relevant articles. In the end, six recurring categories (key success factors) were found, including postgraduate students' teaching and learning methods, quality research supervision mechanisms, building research capacity, library services, workshops by the Postgraduate Student Office, and individual postgraduate students' characteristics (see Table 4).
RESULTS
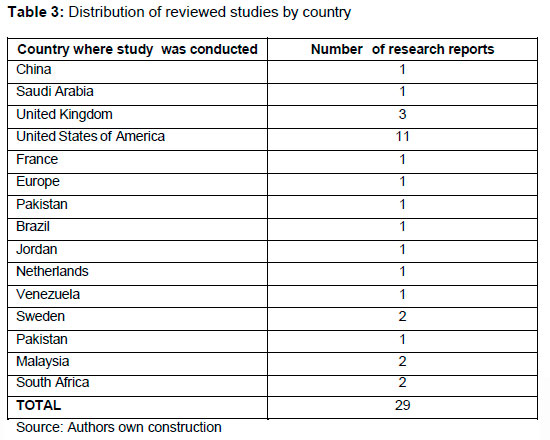
A final 28 studies conducted in 14 countries worldwide were included for review, providing a holistic picture of key factors contributing to academic success in postgraduate studies. A breakdown of the countries and the number of studies reviewed per country is presented in Table 3.
Table 3 shows the distribution of reviewed studies according to countries and the number of research papers reviewed. The first column depicted the names of various countries where this study reviewed their works, while the second column referred to the number of research studies per country used in this article.
Table 4 categorises all the identified key success factors used in this study. Hence, it grouped these success factors alongside the number of authors that wrote on each and provided complexities and strengths.
Table 4 presents significant literature that has addressed the key success factors in postgraduate studies. It identified themes such as quality research supervision, research capacity building, workshops, library services, etc., further discussed below.
The growth in the number of postgraduate students in higher education is a prodigy of increasing importance to researchers, educators, and policymakers worldwide (Young et al. 2013). The themes from Table 4 are further discussed in this section. During the SLR process, this study found that quality research supervision, research capacity building, library services, postgraduate workshop, and the individual characteristics of postgraduate students are the key main success factors in postgraduate studies. These factors are discussed below.
Quality research supervision mechanism
To succeed in postgraduate studies, one must complete a challenging process called quality supervision. Singh (2018) discovered that strong supervisor-student ties increase postgraduate students' talents and raise the likelihood that they will succeed academically. Supervisors encounter their first set of challenges due to postgraduate students' academic and psychological growth, particularly regarding issues with insufficient research knowledge and skills. Doctoral students are more likely to succeed if they are 35 years or older (Hadi and Muhammad 2019). Additionally, it has been determined that poor communication between the supervisor and the student and the participants makes it difficult to complete research projects correctly, effectively, and satisfactorily (Lynch et al. 2018). Having a supervisor who is approachable, accessible, and supportive could contribute to the academic success of postgraduate students.
Success in postgraduate study depends on good supervision, which is challenging. Singh (2018) discovered that a close supervisor-student interaction improves postgraduate student skills and increases the likelihood of obtaining academic success. Poor communication between the supervisor, the student, and the participants hampers the adequate, efficient, and gratifying completion of research projects. As a result, in their interactions, expectations, and responsibilities, both instructors and students must always uphold professional and ethical standards (Muthukrishnan et al. 2022).
Research capacity building
Postgraduate students are expected to engage in creative and collaborative research. Thus, it is indisputable that postgraduate students have many demands and expectations placed on them, particularly those who enrol in research-based programmes (Muthukrishnan et al. 2022). Students pursuing postgraduate degrees at institutions with strong research capabilities are more likely to succeed than those studying such degrees at institutions with poor research capabilities. Dericks et al. (2019) note that helpful supervisors were primarily responsible for satisfying PhD students, particularly when they extended their support in the non-academic aspects of students' lives.
Library services
For postgraduate studies to be successful, access to library services is essential. In addition to being crucial information providers for the industry, postgraduate scholars have the potential to disseminate knowledge to other scholars (Salimi, Bekkers and Frenken 2015). Understanding important success determinants is crucial because they impact students' capacity to successfully complete their programmes on time, especially considering the increased cost of graduate education and the declining resources for higher education in most nations (Rasul and Singh 2017). Therefore, motivation for students enrolled in postgraduate programmes is crucial because little learning occurs without it. More resources, efficient management practices, and highly motivated teachers are available. Ali et al. (2013) revealed a direct correlation between students' performance and institutions with good library resources.
Workshops by the Postgraduate Student Office
Workshops may empower postgraduates and provide favourable results. To understand complicated labour and knowledge processes assisted by technology, workshops offer a platform to help academics identify and explore significant elements in a given domain (Orngreen and Levinsen 2017). Workshops that put psychological empowerment, resilience, emotional intelligence, and spiritual well-being at the centre of postgraduate curriculum development may considerably affect student achievement.
Individual characteristics of postgraduate students
Baporikar (2022) found that a student's past academic success, psychological health, and intellectual prowess are among the traits of postgraduate students. The students' characteristics significantly impact their success in postgraduate courses. Moreover, their aptitude and ability in learning techniques, research techniques, and motivation significantly contribute to their success. Students' self-efficacy could help them to plan effectively and maintain discipline. In this context, self-efficacy refers to a postgraduate student's ability or capacity to achieve a desired goal and graduate on schedule. Students with low self-efficacy frequently exaggerate how challenging their assignments are.
In contrast, those with higher levels of self-efficacy often feel more motivated and effective. A crucial element for the success of postgraduate scholars has been highlighted as belonging to peers on campus or in the classroom (Strayhorn 2019). Belonging can impact postgraduate students' academic success, aspirations, level of academic adjustment, and dedication to a university.
LIMITATION OF THE STUDY
The limitation of this study was seen in the methodology, as it only used a literature review in its data collection as opposed to empirical data collection. A more detailed empirical study can adopt these key success factors found in this study and perform an investigation or a post-factor analysis. This will create more robust findings and the need to develop a framework that will enable postgraduate students to adopt these key success factors in their studies.
CONCLUSION
This study aimed to identify key success factors related to postgraduate studies through an SLR approach. This study opines that postgraduate students struggle to succeed in their research supervision. Hence, some of them drop out. Supervisors and mentors also have roles to play in ensuring the success of postgraduate students. This is due to postgraduate students being depressed with their studies and thus finding it difficult to complete their studies. A thorough analysis of literature sources through a PRISMA approach served as the framework for this review's reporting. The good research capacity, effective supervision mechanisms, funding opportunities, library services, teaching and learning strategies, workshops offered by the Postgraduate Student Office, and individual characteristics of postgraduate students are key success factors more frequently associated with postgraduate studies.
RECOMMENDATIONS
The study recommends that a postgraduate student's ability to function effectively depends on adequately implementing and managing key success factors. Funding a postgraduate study is also paramount as it provides students with finances to collect data, analyse it, and finalise their projects. In most cases, compulsory workshops should be provided by the supervisors and mentors of the postgraduate students. It will ensure that supervisors and mentors attend to their students' challenges. Moreover, supervisors and mentors will provide support structures to assist students in completing their studies. This study further recommends that universities improve their research capacity to increase the success rate of their postgraduate students.
Universities should also encourage good supervisor-student relationships. Continuously studying key success factors in postgraduate studies retention is essential in HEIs. Hence, this study serves as a baseline for developing a conceptual framework that can integrate these key success factors and conduct a pre-test analysis to confirm the effective implementation of these factors in postgraduate studies.
REFERENCES
Alalwan, Nasser, Waleed Mugahed Al-Rahmi, Osama Alfarraj, Ahmed Alzahrani, Noraffandy Yahaya, and Ali Mugahed Al-Rahmi. 2019. "Integrated Three Theories to Develop a Model of Factors Affecting Students' Academic Performance in Higher Education." IEEE Access 7: 98725-98742. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2928142. [ Links ]
Ali, Shoukat, Zubair Haider, Fahad Munir, Hamid Khan, and Awais Ahmed. 2013. "Factors Contributing to the Students Academic Performance: A Case Study of Islamia University SubCampus." American Journal of Educational Research 1(8): 283-289. https://doi.org/10.12691/education-1-8-3. [ Links ]
Areiqat Ahmad, Alheet Ahmad, Al Adwan Ahmad, and Zamil Ahmad M. Ahmad. 2021. "Critical Success Factors (CSFS) in Higher Education Standards Implementation." International Journal of Entrepreneurship 25(1): 1-21. [ Links ]
Baporikar, Neeta. 2022. "Entrepreneurial Universities Challenges and Critical Success Factors to Thrive." International Journal of Applied Management Theory and Research 4(1). https://doi.org/10.4018/ijamtr.300347. [ Links ]
Beauvais, Audrey M., Julie G. Stewart, Susan DeNisco, and John E. Beauvais. 2014. "Factors Related to Academic Success among Nursing Students: A Descriptive Correlational Research Study." Nurse Education Today 34(6): 918-923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2013.12.005. [ Links ]
Dericks, Gerard, Edmund Thompson, Margaret Roberts, and Florence Phua. 2019. "Determinants of PhD Student Satisfaction: The Roles of Supervisor, Department, and Peer Qualities." Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education 44(7): 1053-1068. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2019.1570484. [ Links ]
Frantz, Jose M., Jill Cupido-Masters, Faranha Moosajee, and Mario Smith. 2022. "Non-Cognitive Support for Postgraduate Studies: A Systematic Review." Frontiers in Psychology 12(1). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.773910. [ Links ]
Hadi, Noor Ul and Barudin Muhammad. 2019. "Factors Influencing Postgraduate Students' Performance: A High Order Top down Structural Equation Modelling Approach." Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice 19(2). https://doi.org/10.12738/estp.2019.2.004. [ Links ]
Ham-Baloyi, Wilma ten, and Portia Jordan. 2016. "Systematic Review as a Research Method in PostGraduate Nursing Education." Health SA Gesondheid 21(12): 120-128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hsag.2015.08.002. [ Links ]
Han, Yu, Daniel Gulanowski, and Greg J. Sears. 2022. "International Student Graduates' Workforce Integration: A Systematic Review." International Journal of Intercultural Relations 86: 163-189. [ Links ]
Honig, Meredith I. and Lydia R. Rainey. 2019. "Supporting Principal Supervisors: What Really Matters?" Journal of Educational Administration 57(5): 445-462. https://doi.org/10.1108/jea-05-2019-0089. [ Links ]
Kismihók, Gábor, Darragh McCashin, Stefan T. Mol, and Brian Cahill. 2022. "The Well-Being and Mental Health of Doctoral Candidates." European Journal of Education 57(3): 410-423. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejed.12519. [ Links ]
Lynch, M. F., N. R. Salikhov, and A. B. Salikhova. 2018. "Internal Motivation Among Doctoral Students: Contributions from the Student and from the Student's Environment." International Journal of Doctoral Studies 13: 255-272. [ Links ]
Matus, Janine, Ashlea Walker, and Sharon Mickan. 2018. "Research Capacity Building Frameworks for Allied Health Professionals - A Systematic Review." BMC Health Services Research 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-018-3518-7. [ Links ]
Molson, Alex Rabson. 2022. "Perception of Postgraduate Students Towards the Quality of Library Services Provided at Mzuzu University." PhD Dissertation, Mzuzu University. [ Links ]
Munna Afzal Sayed and Md Abul Kalam. 2021. "Teaching and Learning Process to Enhance Teaching Effectiveness: Literature Review." International Journal of Humanities and Innovation (IJHI) 4(1): 1-4. https://doi.org/10.33750/ijhi.v4i1.102. [ Links ]
Muthukrishnan, Priyadarshini, Kaur Sidhu Gurnam, Teoh Sian Hoon, Narayanan Geethanjali, and Chan Yuen Fook. 2022. "Key Factors Influencing Graduation on Time among Postgraduate Students: A PLS-SEM Approach." Asian Journal of University Education 18(1): 51. https://doi.org/10.24191/ajue.v18i1.17169. [ Links ]
Nzewi, H. N., O. M. Chiekezie, and M. A. Ikon. 2012. "Time Management and Academic Performance of Postgraduate Students in Nigerian Universities." Review of Public Administration and Management 01(2). https://doi.org/10.4172/2315-7844.1000110. [ Links ]
0rngreen, Rikke and Karin Twedelld Levinsen. 2017. "Workshops as a Research Methodology." The Electronic Journal of e-Learning 15(1): 70-81. [ Links ]
Rasul Aamir and Diljit Singh. 2017. "The Role of Academic Libraries in Facilitating Postgraduate Students' Research." Malaysian Journal of Library & Information Science 15(3): 75-84. [ Links ]
Salimi Negin, Rudi Bekkers, and Koen Frenken. 2015. "Does Working with Industry Come at a Price? A Study of Doctoral Candidates' Performance in Collaborative vs. Non-Collaborative Ph.D. Projects." Technovation 41-42(7): 51-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2015.03.007. [ Links ]
Salimi Negin, Rudi Bekkers, and Koen Frenken. 2016. "Success Factors in University-Industry PhD Projects." Science and Public Policy 2, scv076. https://doi.org/10.1093/scipol/scv076. [ Links ]
Sheldon, Elena, Melanie Simmonds-Buckley, Claire Bone, Thomas Mascarenhas, Natalie Chan, Megan Wincott, Hannah Gleeson, Karmen Sow, Daniel Hind, and Michael Barkham. 2021. "Prevalence and Risk Factors for Mental Health Problems in University Undergraduate Students: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis." Journal of Affective Disorders 287(1): 282-292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.03.054. [ Links ]
Sidhu, Gurnam Kaur, Sarjit Kaur, Chan Yuen Fook, and Farhana Wan Yunus. 2013. "Postgraduate Supervision: Exploring Malaysian Students' Experiences." Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 90(10): 133-141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.07.074. [ Links ]
Singh, Jasvir Kaur Nachatar. 2018. "What Are the Factors That Contribute to Postgraduate International Students' Academic Success? A Malaysian Qualitative Study." Higher Education Research & Development 37(5): 1035-1049. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2018.1467383. [ Links ]
Soumana, Almoustapha Oumarou and Mohammad Rahim Uddin. 2017. "Factors Influencing the Degree Progress of International PhD Students from Africa: An Exploratory Study." Üniversitepark Bülten 6(1): 79-94. https://doi.org/10.22521/unibulletin.2017.61.7. [ Links ]
Strayhorn, Terrell L. 2019. "Sense of belonging and student success at historically black colleges and universities: A key to strategic enrolment management and institutional transformation." In Examining Student Retention and Engagement Strategies at Historically Black Colleges and Universities, ed. Samuel L. Hinton and Antwon D. Woods, 32-52. Hershey: IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-7021-9.ch003. [ Links ]
Van Rooij, E., M. Fokkens-Bruinsma, and E. Jansen. 2019. "Factors That Influence PhD Candidates' Success: The Importance of PhD Project Characteristics." Studies in Continuing Education 8: 120. https://doi.org/10.1080/0158037x.2019.1652158. [ Links ]
Wells, Rebecca. 2021. "Session 6C | Paper 1 Critical Success Factors for Postgraduate Distance Education Courses in the UK: A Systematic Review of the Literature - Learning at City." Blogs.city.ac.uk. https://blogs.city.ac.uk/learningatcity/learning-at-city-conference-2021/session-6c-paper-1-critical-success-factors-for-postgraduate-distance-education-courses-in-the-uk-a-systematic-review-of-the-literature. (Accessed 1 December 2023. [ Links ])
Young, Tony J., Peter G. Sercombe, Itesh Sachdev, Rola Naeb, and Alina Schartner. 2013. "Success Factors for International Postgraduate Students' Adjustment: Exploring the Roles of Intercultural Competence, Language Proficiency, Social Contact and Social Support." European Journal of Higher Education 3(2): 151-171. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568235.2012.743746. [ Links ]














