Servicios Personalizados
Articulo
Indicadores
Links relacionados
-
 Citado por Google
Citado por Google -
 Similares en Google
Similares en Google
Compartir
South African Journal of Chemistry
versión On-line ISSN 1996-840X
versión impresa ISSN 0379-4350
S.Afr.j.chem. (Online) vol.67 Durban ene. 2014
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Nano-TiCl4.SiO2: a versatile and efficient catalyst for synthesis of dihydropyrimidones via Biginelli condensation
Bi Bi Fatemeh Mirjalili*; Leila Zamani
Department of Chemistry, College of Science, Yazd University, Iran
ABSTRACT
Nano-TiCl4.SiO2 has been found to be an extremely efficient catalyst for the preparation of 3,4-dihydropyrimidinones/thiones via three-component reactions of an aldehyde, β-ketoester or β-diketone and urea or thiourea under mild conditions. Nano-TiCl4.SiO2 as a solid Lewis acid has been synthesized by reaction of nano-SiO2 and TiCl4. The structural characterization of this acid has been studied by FT-IR (ATR), XRD, SEM and TEM. This process was simple and environmentally benign with high to excellent yields. Furthermore, the catalyst could be recovered conveniently and reused for at least three times.
Keywords: Nano-TiCl4.SiO2, heterogeneous catalyst, multi-component reaction, β-ketoester, β-diketone, urea.
1. Introduction
The Biginelli reaction is an acid-catalyzed, three component, reaction between an aldehyde, β-ketoester or β-diketone and urea or thiourea. Dihydropyrimidinones (DHPMs) and their derivatives have attracted considerable interest due to their wide spectra of biological activities such as antiviral,1 antitumor,2 antibacterial,3 anti-inflammatory4 and antihypertensive.5 The multi-component DHPM-yielding Biginelli reaction was first established in 1893 and was ignored for many years until recently.6
Particular enantiomers are progressively more important for drug applications. Chiral detection allows one enantiomer to treat a disease, while another one may be harmfull.7 An asymmetric carbon exists at the 4-position of the dihydropyrimidone ring and they are generally formulated as racemic mixtures. The absolute configuration in the centre of the molecule can have important biological and pharmacological effects. In many cases chiral dihydropyrimidones have exhibited higher activities or, in the case of enantiomers, a contrary pharmacological activity.8
Recently, significant efforts have been made to find new procedures to deliver DHPMs in good yields. A large number of optimized procedures have been reported where most of the protocols employ various catalytic methods in order to synthesize DHPMs. These protocols utilize Lewis acids or metal-based catalysts such as Ag3PW12O40,9 LaCl3.7H2O10 La(OTf)3,11 Yb(OTf)3,12 ZrCl4,13 BiCl3,14 Mn(OAc)3,15 LiClO4,16 H3BO3,17 CeCl3/InCl318, Al(HSO4)3,19 KHSO4,20 ZnI2,21 trichloroisocyanuric acid (TCCA),22 zeolite23 and HBF4.24 However, each method has certain restrictions with regard to scope and reaction conditions; For example, costs of synthesis, unrecoverable catalysts, strong acidic conditions, long reaction times, low yields, difficult work-up and harsh reaction conditions. To avoid these limitations, we have investigated the use of nano-TiCl4.SiO2.
2. Experimental
2.1. General
The chemicals were obtained form Merck Company and used without any additional purification. The products were characterized by FT-IR (ATR), 1H NMR, and a comparison of their physical properties with those reported in the literature was made. FT-IR (ATR) spectra were recorded on a Bruker, Eqinox 55 spectrometer. A Bruker (DRX-400 Avance) NMR was used to record the 1H NMR spectra. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of materials were recorded by employing a Philips Xpert MPD diffractometer equipped with a Cu Kα anode (λ = 1.54 Å) in the 2ϴ range from 10 to 80 °. The SEM of nano particles was determined with a VEGA/TESCAN scanning electron microscope and the TEM photograph was prepared on a Leo 912AB OMEGA microscope.
2.2. General Method for the Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidinones/thiones
A mixture of aldehyde (2 mmol), ethyl acetoacetate/ acetylaceton (2 mmol), urea/thiourea (2.5 mmol) and nano-TiCl4.SiO2 (0.05 g) was heated with stirring at 60 °C for 18 minutes. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC (chloroform:petroleum ether, 80:20). After completion of the reaction, the mixture was cooled to room temperature and diluted with acetone. The catalyst was recovered by filtration and washed with acetone (2x5 mL). The solvent was evaporated and the crude product recrystallized from 85 % ethanol. All the products were identified by comparison of their physical and spectral data with those of authentic samples.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one (Table 3, Entry 1)
Yield 90 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloroform:petroleum ether, 80:20, Rf = 0.4); M.p. 218-219 °C (221 °C)31, FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3367, 3235, 1697, 1644, 1475, 1608, 1580, 1521, 1445, 1360, 1338, 1088, 1220, 783 cm-1.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-3,4-dihydropyri-midin-2(1H)-one (Table 3, Entry 2)
Yield 95 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloro-form:petroleum ether, 80:20, Rf = 0.4); M.p. 210-211 °C (211 °C)31; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3229, 3112,1725,1698,1642,1597,1489,1594, 1518, 1518, 1462, 1374, 1347, 1290, 1084, 1210, 855 cm-1,1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): 1.10 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 4.0 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 5.38 and 5.39 (s, 1H), 7.01 (s, Nh), 7.44 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 8.07 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 8.86 (s, NH) ppm.
4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-5-ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin2(1H)-on (Table 3, Entry 3)
Yield 91 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloroform:petroleum ether, 80:20, Rf = 0.4); M.p. 211-214 °C (211-213 °C)30; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3238, 3116, 1721, 1699, 1645, 1460, 1594, 1577, 1423, 1367, 1289, 1085, 1217, 779, 683 cm-1.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one (Table 3, Entry 4)
Yield 80 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloro-form:petroleum ether, 80:20, Rf = 0.5); M.p. 201-204 °C (203 °C)31; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3237, 3116,1722, 1702, 1647, 1511, 1588, 1583, 1541, 1458, 1367, 1251, 1086, 1218, 1031, 1277, 779 cm-1,1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, ppm): 1.20 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 4.10 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.12 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 5.36 and 5.37 (s, 1H), 6.12 (s, NHH), 6.85 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.25 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 8.61 (s, NH) ppm.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-3,4-dihydropyri midin-2(1H)-one (Table 3, Entry 5)
Yield 90 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol,TLC -chloroform: petroleum ether, 80:20, Rf = 0.5); M.p. 202-203 °C (205-207 °C)41 FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3237, 3108, 1699, 1650, 1494, 1598, 1550, 1522, 1460, 1375, 1275, 1257, 1091, 1223, 1038, 697, 772, 862 cm-1.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one (Table 3, Entry 6)
Yield 89 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloro-form:petroleum ether, 80:20, Rf = 0.3); M.p. 215-218 °C (214 °C)31; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3233, 3114, 1724, 1701, 1646, 1514, 1586, 1580, 1519, 1460, 1370, 1286, 1086, 1218, 777 cm-1.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-phenyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2 (1H)-one (Table 3, Entry 7)
Yield 86 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloro-form:petroleum ether, 80:20, Rf = 0.3); M.p. 205-206 °C (204 °C)31; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3240, 3122, 1722, 1698, 1645, 1486, 1600, 1599, 1586, 1464, 1340, 1271, 1088, 1218, 699, 757 cm-1, 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): 1.19 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 2.36 (s, 3H), 4.10 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.11 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 5.421 and 5.426 (s, 1H), 6.07 (s, NH), 7.27-7.34 (m, 5H), 8.52 (s, NH) ppm.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-phenethyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2 (1H)-one (Table 3, Entry 8)
Yield 89 % (Recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloro-form:petroleum ether, 80:20, Rf = 0.27); M.p. 155-157 °C (252-153 °C)40; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3242, 3200, 1722, 1702, 1650, 1494, 1605, 1552, 1454, 1360, 1089, 1287, 1223, 695, 773 cm-1, 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): 1.28 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.93 (m, 2H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 2.69 (m, 1H), 2.80 (m, 1H ), 4.19 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H),4.20 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.37and 4.38 (t, 1H), 6.15 (s, NH), 7.20 (m, 3H), 7.30 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 8.35 (s, NH) ppm.
5-Methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-phenyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-thione (Table 3, Entry 9)
Yield 80 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloroform: petroleum ether, 70:30, Rf = 0.3); M.p. 181-182 °C (184 °C)37; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3277, 3178, 1613, 1453, 1613, 1525, 1385, 1362, 1330, 1116, 694, 774 cm-1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, ppm): 2.06 and 2.08 (s, 3H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 5.36 and 5.37 (s, 1H), 7.20-7.29 (m, 5H), 8.64 (s, NH), 9.18 (s, NH) ppm.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-styryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2 (1H)-one (Table 3, Entry 10)
Yield 92 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloroform:petroleum ether, 80:20, Rf = 0.31); M.p. 229-230 °C (232-233 °C)39; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3239, 3113, 1721, 1698, 1650, 1486, 1602, 1583, 1463, 1366, 1286, 1089, 1223, 692, 755 cm-1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) 1.31 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 4.21 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.23 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 5.00 and 5.02 (s, 1H), 5.66 (s, NH), 6.23 (dd, J = 15.8 and 6.4 Hz, 1H), 6.51 (d, J = 15.8 Hz, 1H), 7.24 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 7.37 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 7.6 (s, NH) ppm.
4-(2-Chloro-5-nitrophenyl)-5-ethoxycarbonyl-6-phenyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-thione (Table 3, Entry 11)
Yield 78 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloro-form:petroleum ether, 70:30, Rf = 0.55); M.p. 236-238 °C (239 °C)38; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3257, 1666, 1494, 1602, 1551, 1525, 1440, 1398, 1375, 1344, 1344, 1063, 1199, 1142, 698 cm-1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) 0.84 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 3.87 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 6.05 and 6.06 (s, 1H), 7.49-7.54 (m, 5H), 7.57 (s, NH), 7.67 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 8.0 (s, NH), 8.20 (dd, J = 8.7 and 2.6 Hz, 1H), 8.35 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H) ppm.
4-(4-N,N-Dimethylaniline)-5-(ethoxycarbonyl)-6-methyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-thione (Table 3, Entry 12)
Yield 89 % (Recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloroform:petroleum ether, 70:30, Rf = 0.33); M.p. 209-210 °C (not found); FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3273, 3160, 1701, 1447, 1596, 1523, 1473, 1411, 1361, 1314, 1314, 1091, 1278, 1124, 814 cm-1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) 1.13 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 2.87 (s, 6H), 4.0 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 5.22 and 5.23 (s, 1H), 5.99 (s, NH), 6.63 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.14 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 8.35 (s, NH) ppm.
4-(4-N,N-Dimethylaniline)-5-(ethoxycarbonyl)-6-methyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one (Table 3, Entry 13)
Yield 94 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloro-form:petroleum ether, 70:30, Rf = 0.35); M.p. 253-255 °C (250 °C)42; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3235, 3200, 1719, 1699, 1647, 1461, 1618, 1563, 1525, 1458, 1365, 1312, 1254, 1088, 1217, 783 cm-1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) 1.22 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 2.38 (s, 3H), 2.98 (s, 6H), 4.12 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.14 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 5.33 and 5.34 (s, 1H), 6.74(d,J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.20 (m, 2H and Nh), 7.82 (s, NH) ppm.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-thione (Table 3, Entry 14)
Yield 83 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloro-form:petroleum ether, 70:30, Rf = 0.3); M.p. 191-193 °C (not found); FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3320, 3173, 1670, 1573, 1510, 1462, 1395, 1370, 1327, 1030, 1174, 1116, 810 cm-1, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, ppm): 1.20 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 2.34 (s, 3H), 2.37 (s, 3H), 4.10 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.11 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 5.36 and 5.37 (s, 1H), 7.13 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.19 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 8.01 (s, NH), 8.64 (s, NH) ppm.
4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-3,4-dihydropyri midin-2(1H)-thione (Table 3, Entry 15)
Yield 77 % (Recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloroform:petroleum ether, 70:30, Rf = 0.3); M.p. 206-209 °C (208 °C)38; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3278, 3179, 1619, 1452, 1586, 1385, 1361, 1328, 1118, 828, 725 cm-1.
5-Acetyl-6-methyl-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-thione (Table 3, Entry16)
Yield 82 % (Recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloroform:petroleum ether, 70:30, Rf = 0.45); M.p. 161-162 °C (161-163 °C)38; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3309, 3232, 1618, 1458, 1563, 1509, 1380, 1363, 1326, 1235, 1110, 1023, 828 cm-1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, ppm): 2.16 (s, 3H), 2.38 (s, 3H), 3.82 (s, 3H), 5.43 (s, 1H), 6.90 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.18 (s, NH), 7.23 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H)), 7.63 (s, NH) ppm.
4,6-Diphenyl-5-ethoxycarbonyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-thione (Table 3, Entry 17)
Yield 87 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloro-form:petroleum ether, 70:30, Rf = 0.3); M.p. 184-185 °C (183-185 °C)38; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3313, 3152, 1672, 1641, 1492, 1600, 1566, 1458, 1367, 1334, 1107, 1203, 1130, 692, 763 cm-1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d60.85 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 3.88 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 3.89 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 5.57 and 5.58 (s, 1H), 7.36-7.50 (m,10H and Nh), 7.83 (s, NH) ppm.
5-Ethoxycarbonyl-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-phenyl-3,4-dihydropyrimi-din-2(1H)-thione (Table 3, Entry 18)
Yield 90 % (recrystallized from 85 % ethanol, TLC - chloroform:petroleum ether, 70:30, Rf = 0.45); M.p. 152-153 °C (151152 °C)38; FT-IR: vmax (KBr) = 3304, 3251, 1672, 1612, 1511, 1452, 1375, 1373, 1339, 1253, 1096, 1172, 1133, 1050, 824 cm-1.
3. Results and Discussion
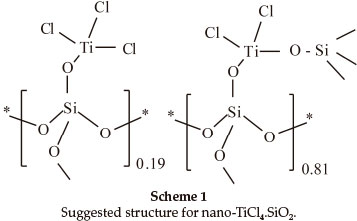
Nano-TiCl4.SiO225,26 as an efficient and reusable acidic catalyst is synthesized via the reaction of nano-silica gel with TiCl4 in chloroform at room temperature. Recently, our study on the structure of nano-TiCl4.SiO2 has led to more exactly configuration containing SiO2-TiCl3 (19 %) and SiO2-TiCl2-SiO2 (81 %) as demonstrated in Scheme 1.
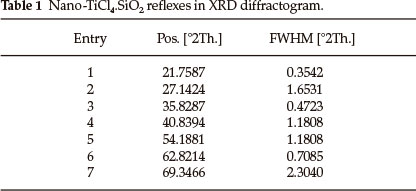
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of nano-SiO2 and nano-TiCl4.SiO2 are shown in Fig. 1. According to the Scherrer equation,27 the broadening of peaks implies a decrease in crystalline size. The XRD pattern of nano-SiO2 exhibits a strong peak at a2θ value of 21.8024 ° with FWHM equal to 0.1771. From the XRD data of nano-TiCl4.SiO2, the values of 2θ and FWHM are presented in Table 1. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of nano-TiCl4.SiO2 are shown in Fig. 2. The particle size in the TEM pattern was calculated to be 14-20 nm using the GetData Graph program.

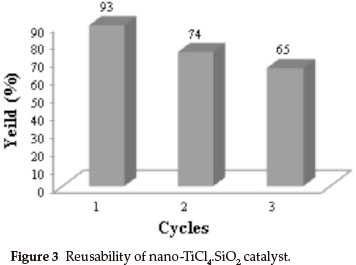
For an investigation of the efficiency of nano-TiCl4.SiO2 in preparation of racemic 5-ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-phenyl-3-4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one, we examined the reaction of benzaldehyde (2 mmol, 0.21 mL), ethyl acetoacetate (2 mmol, 0.26 mL), urea (2.5 mmol, 0.15 g) as model reaction (Scheme 2). The reaction under different conditions in the presence of TiCl4.SiO2 or nano-TiCl4.SiO2 revealed that the best conditions were 0.12 g of TiCl4.SiO2 or 0.05 g of nano-TiCl4.SiO2 under solvent-free conditions at 60 °C (Table 2, Entries 1 and 9). Once the scope of the reaction condition was established, the reusability of catalyst was examined. After performing the reaction, the catalyst was separated, washed with acetone, dried and re-used up to three times in the same reaction without losing its activity (Fig. 3). This reaction was effectively scaled up to more than 10 grams of product.
Next, the applicability of this procedure was explored using a wide range of aromatic aldehydes containing electron-donating or electron-withdrawing groups (Table 3, Scheme 3). The three-component reaction proceeded smoothly to give the corresponding racemic 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones/thiones in moderate to good yields. In all cases, aromatic aldehydes containing electron-withdrawing groups gave higher yields of products in shorter times than aromatic aldehydes containing electron-donating groups (Table 3, Entries 2 and 4).
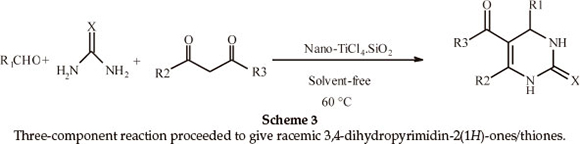
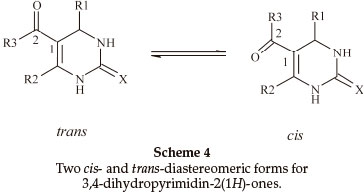
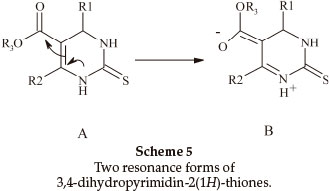
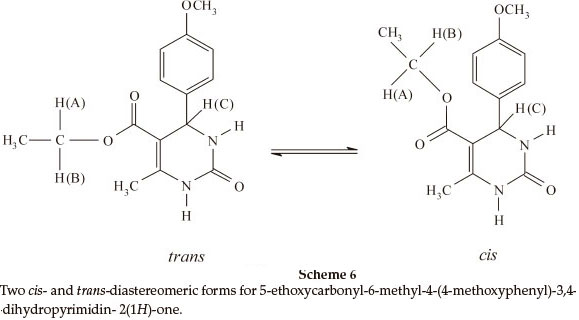
Biginelli products have an a,b-unsaturated carbonyl group giving rise to cis- and trans-diastereomers due to sigma bond rotation around C1-C2 (Scheme 4). In the FT-IR spectra of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones containing an ester group, three carbonyl signals were observed. Two of them at ~1700 cm-1 are related to the α,β-unsaturated ester carbonyl group and the third signal nearly 1650 cm-1 is related to a urea type carbonyl band. In the FT-IR spectra of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin- 2(1H)-thiones, only one stretching band is observed for the α,β-unsaturated ester carbonyl group nearly 1670 cm-1. This indicates that the thiones are only in the trans form (Scheme 5). In the 1H NMR spectra of some compounds such as 5-ethoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-pyrimidin-2(1H)-one, the CH2 protons H(A) and H(B) are observed as two quartet peaks at 4.10 and 4.12 ppm integrating for two protons; H(C) is observed as two singlet peaks at 5.36 and 5.37 ppm integrating for one proton (Scheme 6).
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, nano-TiCl4.SiO2 is an efficient, cheap, non-corrosive, easily available, and reusable catalyst for the synthesis of racemic dihydropyrimidin-ones or thiones. The present procedure describes a useful improvement in the existing conditions for the Biginelli condensation. High to excellent yields, ease of work-up, mild reaction conditions, short reaction times, environmentally friendly procedures and the ability to tolerate a diversity of aldehyde substituents are attractive features of this new procedure.
Acknowledgements
The Research Council of Yazd University and the Central Iron Ore and Strategic of Research Centre are gratefully acknowledged for the financial support of this work.
References
1 P. Sanjeev and G.S. Gokavi, Catal. Commun., 2007, 8, 279-284. [ Links ]
2 (a) D. Nagarathnam, S.W. Miao, B. Lagu, M.C. Harrell, K.P. Vyas and C. Gluchowski, J. Med. Chem., 1999, 42, 4764-4777. [ Links ] (b) J.C. Barrow, P.G. Nantermet, D. Nagarathnam and C. Forray, J. Med. Chem., 2000, 43, 2703-2718. [ Links ]
3 C.O. Kappe, Tetrahedron, 1993, 49, 6937-6963. [ Links ]
4 G.I. Grover, S. Dzwonczyk, D.M. McMullen, D.E. Normadin, C.S. Parham, P.G. Sleph and S.J. Moreland, J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 1995, 26, 289-291. [ Links ]
5 K.S. Atwal, G.C. Rovnyak, J. Schwartz, S. Moreland, A. Hedberg, J.Z. Gougoutas, M.F. Malley and D.M. Floyd, J. Med. Chem., 1990, 33, 1510-1515. [ Links ]
6 P.G. Biginelli, Gazz. Chem. Ital, 1893, 23, 360-413. [ Links ]
7 Z. Dai, C.U. Pittman, Jr and T. Li, Chirality, 2013, 25, 238-242. [ Links ]
8 S. Goldmann, J. Stoltefuss and L. Born, J. Med. Chem., 1992, 35, 3341-3344. [ Links ]
9 J.S. Yadav, B.V.S. Reddy, N. Lingaiah and P.S. Saiprasad, Eur.J.Org. Chem., 2004, 3, 552-557. [ Links ]
10 J. Lu, Y. Bai, Z. Wang, B. Yang and H. Ma, Tetrahedron Lett, 2000, 41, 9075-9078. [ Links ]
11 R.F. Chen and C.T. Qian, Chin. J. Chem, 2002, 20, 427-430. [ Links ]
12 Y. Ma, C. Qian and M. Wang, J. Org. Chem, 2000, 65, 3864-3868. [ Links ]
13 C.V Reddy, M. Mahesh, P.VK. Raju, T.R. Babu and VVN. Reddy, Tetrahedron Lett, 2002, 43, 2657-2659. [ Links ]
14 K. Ramalinga, P. Vijayalakshmi and T.N.B. Kaimal, Synlett, 2001, 6, 863-865. [ Links ]
15 K.A. Kumar, M. Kasthuraiah, C.S. Reddy and C.D. Reddy, Tetrahedron Lett, 2001, 42, 7873-7875. [ Links ]
16 J.S. Yadav, B.VS. Reddy, R. Srinivas, C. Venugopal and T. Romalingam, Synthesis, 2001, 1341-1345. [ Links ]
17 T. Shujang, F. Fang, M. Chunbao, J. Hong, F. Youjian, S. Daquing and W. Xiangshan, Tetrahedron Lett, 2003, 44, 6153-6155. [ Links ]
18 O. Muniz-Muniz and E. Juaristi, Arkivoc, 2003, 9, 16-26. [ Links ]
19 S. Tu, F. Fang, C. Zhu, T. Li, X. Zhang and Q. Zhang, Synlett, 2004, 3, 537-539. [ Links ]
20 M.M. Khodaei, P. Salehi, M.A. Zolfigol and S. Sirouszadeh, Polish. J. Chem., 2004, 78, 385-388. [ Links ]
21 G. Jenner, Tetrahedron Lett, 2004, 45, 6195-6198. [ Links ]
22 M.A. Bigdeli, S. Jafari, G.H. Mahdavinia and H. Hazarkhani, Catal. Commun., 2007, 8, 1641-1644. [ Links ]
23 M. Tajbakhsh, B. Mohajerani, M.M. Heravi and A.N. Ahmadi, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2005, 236, 216-219. [ Links ]
24 W. Chen, S.D. Qin and J.R. Jin, Catal. Commun., 2007, 8, 123-126. [ Links ]
25 B.F. Mirjalili, A. Bamoniri and L. Zamani, Scientia Iranica. 2012, 19, 565-568. [ Links ]
26 B.F. Mirjalili, A. Bamoniri and L. Zamani, Lett. Org. Chem., 2012, 9, 338-343. [ Links ]
27 R. Jenkins and R.L. Snyder, Introduction to X-ray Powder Diffractometry, John Wiley & Sons, 1996, 89-91. [ Links ]
28 A. Kumar and R.A. Maurya, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2007, 272, 53-56. [ Links ]
29 P.M. Kumar, K.S. Kumar, S.R. Poreddy, P.K. Mohakhud, K. Mukkanti and M. Pal, Tetrahedron Lett, 2011, 52, 1187-1191. [ Links ]
30 Y. Yu, D. Liu, C. Liu and G. Luo, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2007, 17, 3508-3510. [ Links ]
31 M.M. Heravi, K. Bakhtiari and F.F. Bamaharram, Catal. Commun., 2006, 7, 373-376. [ Links ]
32 H. Adibi, H.A. Samimi and M. Beygzadeh, Catal. Commun., 2007, 8, 2119-2124. [ Links ]
33 C.M. Adharvana and K. Syamasundar, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2004, 221, 137-139. [ Links ]
34 N.S. Nandurkar, M.J. Bhanushali, M.D. Bhor and B.M. Bhanage, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2007, 271, 14-17. [ Links ]
35 B. Ahmed, A. Khan, R. Habibullah and M. Keshari, Tetrahedron Lett., 2009, 50, 2889-2892. [ Links ]
36 X.H. Chen, X.Y. Xu, H. Liu, L.F. Cun and L.Z. Gong, J. Am. Chem. Soc, 2006, 128, 14802-14803. [ Links ]
37 M.M. Amini, A. Shaabani and A. Bazgir, Catal. Commun., 2006, 7, 843-847. [ Links ]
38 J. C. Rodríguez-Domínguez, D. Bernardi and G. Kirsch, Tetrahedron Lett, 2007, 48, 5777-5780. [ Links ]
39 T. Kadre, S.R. Jetti, A. Bhatewara, P. Paliwal and S. Jain, Arch. Appl. Sci. Res., 2012, 4, 988-993. [ Links ]
40 S.D. Sharma, P. Gogoi and D. Konwar, Green Chem., 2007, 9, 153-157. [ Links ]
41 A. Kumar and R.A. Maurya, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2007, 272, 53-56. [ Links ]
Received 24 October 2012
Revised 21 June 2013
Accepted 13 December 2013
* To whom correspondence ahould be addressed. E-mail: fmirjalili@yazd.ac.ir





![Synthesis and characterization of new bis-symmetrical adipoyl, terepthaloyl, chiral diimido-di-L-alanine diesters and chiral phthaloyl-L-alanine ester of tripropoxy p-tert-butyl calix[4]arene and study of their hosting ability for alanine and Na+](/img/es/next.gif)








